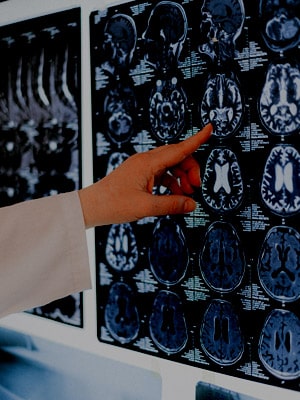
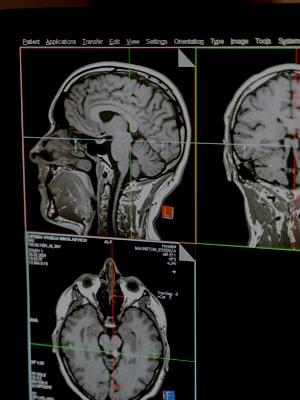
Neuroimaging is a branch of medical imaging that focuses on the brain. In addition to diagnosing disease and assessing brain health, neuroimaging also studies:
- How the brain works
- How various activities impact the brain
Maxlife Diagnostic uses a neuroimaging technique called magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). MRS in our studies allows researchers to obtain biochemical information about the brain, while magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) only provides information about the brain’s structure.